Abstract
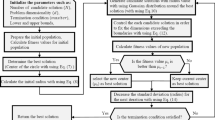
This paper focuses on modification of basic artificial algae algorithm (AAA) for solving binary optimization problems by using a new solution update rule because the agents in AAA work on continuous solution space. The candidate solution generation process of algorithm in the basic version of AAA is replaced with a mechanism that use a neighbor solution randomly selected from the population and three decision variables of this solution. The current solution is taken from the population and randomly selected three dimensions of this solution are changed using the neighbor solution. The agents of AAA work on continuous solution space and this modification for AAA is required for solving a binary optimization problem because a binary optimization problems have decision variables which are element of set {0, 1}. The performance of the proposed algorithm, binAAA for short, is investigated on the uncapacitated facility location problems which are pure binary optimization problem and there is no integer or real valued decision variables in this problem. The results obtained by binAAA are compared with the results of state-of-art algorithms such as artificial bee colony, particle swarm optimization, and genetic algorithms. Experimental results and comparisons show that the binAAA is better than the other algorithm almost all cases in terms of solution quality and robustness based on the mean and standard deviations, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J Glob Optim 39(3):459–471
Uymaz SA, Tezel G, Yel E (2015) Artificial algae algorithm (AAA) for nonlinear global optimization. Appl Soft Comput 31:153–171
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The Whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1997) A discrete binary version of the particle swarm algorithm. In: SMC ‘97 Conference proceedings—1997 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics, vol 1–5, pp 4104–4108
Rodriguez L et al (2017) A fuzzy hierarchical operator in the grey wolf optimizer algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 57:315–328
Kiran MS (2015) TSA: tree-seed algorithm for continuous optimization. Expert Syst Appl 42(19):6686–6698
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A (1996) Ant system: optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 26(1):29–41
Caraveo C, Valdez F, Castillo O (2016) Optimization of fuzzy controller design using a new bee colony algorithm with fuzzy dynamic parameter adaptation. Appl Soft Comput 43:131–142
Uymaz SA, Tezel G, Yel E (2015) Artificial algae algorithm with multi-light source for numerical optimization and applications. Biosystems 138:25–38
Monabbati E, Kakhki HT (2015) On a class of subadditive duals for the uncapacitated facility location problem. Appl Math Comput 251:118–131
Krarup J, Pruzan PM (1983) The simple plant location problem—survey and synthesis. Eur J Oper Res 12(1):36–81
Tan F et al (2008) A genetic algorithm-based method for feature subset selection. Soft Comput 12(2):111–120
Shang L, Zhou Z, Liu X (2016) Particle swarm optimization-based feature selection in sentiment classification. Soft Comput 20(10):3821–3834
Taormina R, Chau KW (2015) Data-driven input variable selection for rainfall-runoff modeling using binary-coded particle swarm optimization and extreme learning machines. J Hydrol 529:1617–1632
Mirhosseini M, Nezamabadi-pour H (2017) BICA: a binary imperialist competitive algorithm and its application in CBIR systems. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0686-4
Kiran MS, Gunduz M (2013) XOR-based artificial bee colony algorithm for binary optimization. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 21:2307–2328
Kiran MS (2015) The continuous artificial bee colony algorithm for binary optimization. Appl Soft Comput 33:15–23
Kashan MH, Nahavandi N, Kashan AH (2012) DisABC: a new artificial bee colony algorithm for binary optimization. Appl Soft Comput 12(1):342–352
Beasley JE (1990) Or-library—distributing test problems by electronic mail. J Oper Res Soc 41(11):1069–1072
Atkinson J, Campos D (2016) Improving BCI-based emotion recognition by combining EEG feature selection and kernel classifiers. Expert Syst Appl 47:35–41
Gunasundari S, Janakiraman S, Meenambal S (2016) Velocity bounded boolean particle swarm optimization for improved feature selection in liver and kidney disease diagnosis. Expert Syst Appl 56:28–47
Khazaei P et al (2016) Applying the modified TLBO algorithm to solve the unit commitment problem. In: 2016 World Automation Congress (Wac)
Kamboj VK (2016) A novel hybrid PSO-GWO approach for unit commitment problem. Neural Comput Appl 27(6):1643–1655
Saravanan B, Kumar C, Kothari DP (2016) A solution to unit commitment problem using fire works algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 77:221–227
Li S et al (2016) Discrete chaotic gravitational search algorithm for unit commitment problem. In: Intelligent computing theories and application, Icic 2016, Pt Ii, vol 9772, pp 757–769
Sun YJ et al (2017) Correlation feature selection and mutual information theory based quantitative research on meteorological impact factors of module temperature for solar photovoltaic systems. Energies 10(1):7
Pavez-Lazo B, Soto-Cartes J (2011) A deterministic annular crossover genetic algorithm optimisation for the unit commitment problem. Expert Syst Appl 38(6):6523–6529
Haddar B et al (2013) A new hybrid heuristic for the 0–1 Knapsack sharing problem. In: Proceedings of 2013 international conference on industrial engineering and systems management (Ieee–Iesm 2013), pp 12–18
Haddar B et al (2015) A hybrid heuristic for the 0–1 Knapsack sharing problem. Expert Syst Appl 42(10):4653–4666
He YC et al (2016) Exact and approximate algorithms for discounted {0–1} knapsack problem. Inf Sci 369:634–647
He YC et al (2018) A novel binary artificial bee colony algorithm for the set-union knapsack problem. Future Gener Comput Syst Int J Esci 78:77–86
Zhu H et al (2017) Discrete differential evolutions for the discounted {0–1} knapsack problem. Int J Bio Inspir Comput 10(4):219–238
Abdel-Basset M, El-Shahat D, Sangaiah AK (2017) A modified nature inspired meta-heuristic whale optimization algorithm for solving 0–1 knapsack problem. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0731-3
Zhang J, Chau KW (2009) Multilayer ensemble pruning via novel multi-sub-swarm particle swarm optimization. J Univers Comput Sci 15(4):840–858
Wang R et al (2017) Incorporating diversity and informativeness in multiple-instance active learning. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 25(6):1460–1475
Yanasse HH, Soma NY (1987) A new enumeration scheme for the Knapsack-problem. Discrete Appl Math 18(2):235–245
James RJW, Nakagawa Y (2005) Enumeration methods for repeatedly solving multidimensional knapsack sub-problems. IEICE Trans Inf Syst E88d(10):2329–2340
Lalami ME, El-Baz D (2012) GPU implementation of the branch and bound method for knapsack problems. In: 2012 IEEE 26th international parallel and distributed processing symposium workshops & Phd Forum (Ipdpsw), pp 1769–1777
Freville A, Plateau G (1994) An efficient preprocessing procedure for the multidimensional 0–1-knapsack problem. Discret Appl Math 49(1–3):189–212
Beasley JE (1990) A Lagrangian heuristic for set-covering problems. Naval Res Logist 37(1):151–164
Tohyama H, Ida K, Matsueda J (2011) A genetic algorithm for the uncapacitated facility location problem. Electron Commun Jpn 94(5):47–54
Pampara G, Engelbrecht AP, Franken N (2006) Binary differential evolution. In: 2006 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, vol 1–6, pp 1858–+
Engelbrecht AP, Pampara G (2007) Binary differential evolution strategies. In: 2007 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, vols 1–10, proceedings, pp 1942–1947
Yuan XH et al (2009) An improved binary particle swarm optimization for unit commitment problem. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):8049–8055
Nezamabadi-pour H (2015) A quantum-inspired gravitational search algorithm for binary encoded optimization problems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 40:62–75
Soleimanpour-moghadam M, Nezamabadi-pour H, Farsangi MM (2014) A quantum inspired gravitational search algorithm for numerical function optimization. Inf Sci 267:83–100
Cinar AC, Kiran MS (2017) Similarity and logic gate-based tree-seed algorithms for binary optimization. Comput Ind Eng 115:631–646
Zhang XD et al (2016) Binary artificial algae algorithm for multidimensional knapsack problems. Appl Soft Comput 43:583–595
Ghosh D (2003) Neighborhood search heuristics for the uncapacitated facility location problem. Eur J Oper Res 150(1):150–162
Holland JH (1992) Genetic algorithms. Sci Am 267(1):66–72
Pampara G, Franken N, Engelbrecht AP (2005) Combining particle swarm optimisation with angle modulation to solve binary problems. In: 2005 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, vol 1–3, proceedings, pp 89–96
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey and Selcuk University Scientific Projects Coordinatorship for their institutional supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korkmaz, S., Babalik, A. & Kiran, M.S. An artificial algae algorithm for solving binary optimization problems. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 9, 1233–1247 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0772-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-017-0772-7